What Is Cryptocurrency Mining?
Cryptocurrency mining is how new transactions are validated on a blockchain’s public ledger. Validating transactions results in a reward of the cryptocurrency on the blockchain – adding new coins into circulation.
How Does Cryptocurrency Mining Work?
A miner is a node in the given blockchain network that collects transactions and organizes them into blocks. Whenever a new transaction occurs miners receive and verify the data of the transaction before sorting it into a memory pool, mempool for short.
Once in the memory pool, transactions are put into a candidate block. If the miner is successful with the following steps the candidate block is added to the blockchain, giving this miner a reward for their efforts.
Step 1 – Hashing Transactions
A miner will take transactions from their memory pool, and put them through a hash function. A hash function turns any piece of data, no matter how big into a fixed size, called a hash. In this context, all of the data of the transaction is turned into a ‘transaction hash’.
Along with this, the miner will create a separate block with a transaction called the coinbase. This separate block will give them their mining reward if their candidate block is successful, although it can contain any arbitrary data.[1]https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Coinbase
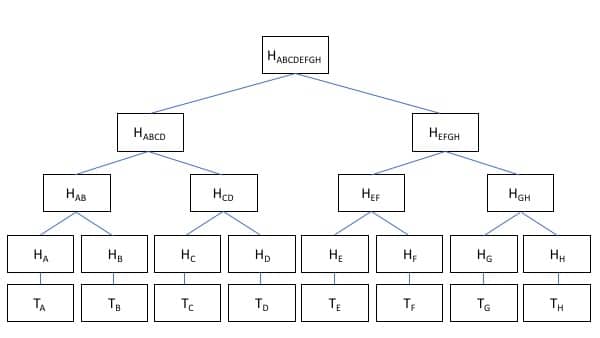
Step 2 – Create A Merkle Tree
After transactions are hashed they’re organized into a Merkle Tree or Hash Tree.
This process links two transactions together, hashes them, and repeats the process over and over until all data is encoded under one singular hash, called the Merkle Root or Root Hash.
Step 3 – Find A Valid Block Hash
To create a valid block hash, a miner has to combine the hash of the previous block, with their root hash, and an arbitrary number called Nonce (number used only once).
The nonce number is changed until a valid hash is found, as the hash of the previous block and the root hash cannot be changed.
In order to be considered valid, the block hash must be less than a certain target value determined in the protocol. In Bitcoin mining, the block hash must start with a certain number of zeros. This is what we call mining difficulty.
What Is Mining Difficulty?
The cryptocurrency mining difficulty is adjusted by the protocol regularly. This ensures that the rate at which new blocks are mined remains constant.
This is what makes the issuance of new coins steady and predictable. The difficulty adjusts in proportion to the amount of computational power or mining hash rate on to the network.
This means as more miners join the network the hashing difficulty gets harder. Likewise, if miners leave the hashing difficulty is easier. Allowing for a steady flow of blocks being mined.
Step 4 – Broadcast The Block
Once a miner finds a valid block hash, the miner who found it will broadcast it to the entire network of other miners/nodes. The nodes will confirm that the block and its hash are valid. If they find it is valid, the block is added to their copy of the blockchain.
The previous candidate block has now become a confirmed block. The miners now move on to the next block. The miners whose candidate blocks weren’t successful discard it and repeat the process in hopes of having the next confirmed block.
References



